Knee clearance is a fundamental aspect of accessible design that ensures individuals with disabilities can comfortably access essential fixtures like sinks, countertops, and desks. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) sets forth specific guidelines that learn about ada knee space here dictate the required knee clearance dimensions, promoting independence and usability for all. This article explores the importance of , the relevant requirements, and effective strategies for implementing these standards in various environments.
Why Knee Clearance Matters
Knee clearance is vital for enabling individuals using wheelchairs or mobility devices to engage fully with their surroundings. Properly designed spaces allow users to perform daily activities—such as washing hands, cooking, or working—without facing physical barriers. Ensuring adequate knee clearance fosters a sense of autonomy and dignity, making it essential in public facilities, workplaces, and residential settings.
ADA Requirements for Knee Clearance
- Height Specifications: The ADA requires that the minimum height for knee clearance should be 27 inches from the floor. This height allows wheelchair users to roll comfortably under counters and sinks, facilitating access.
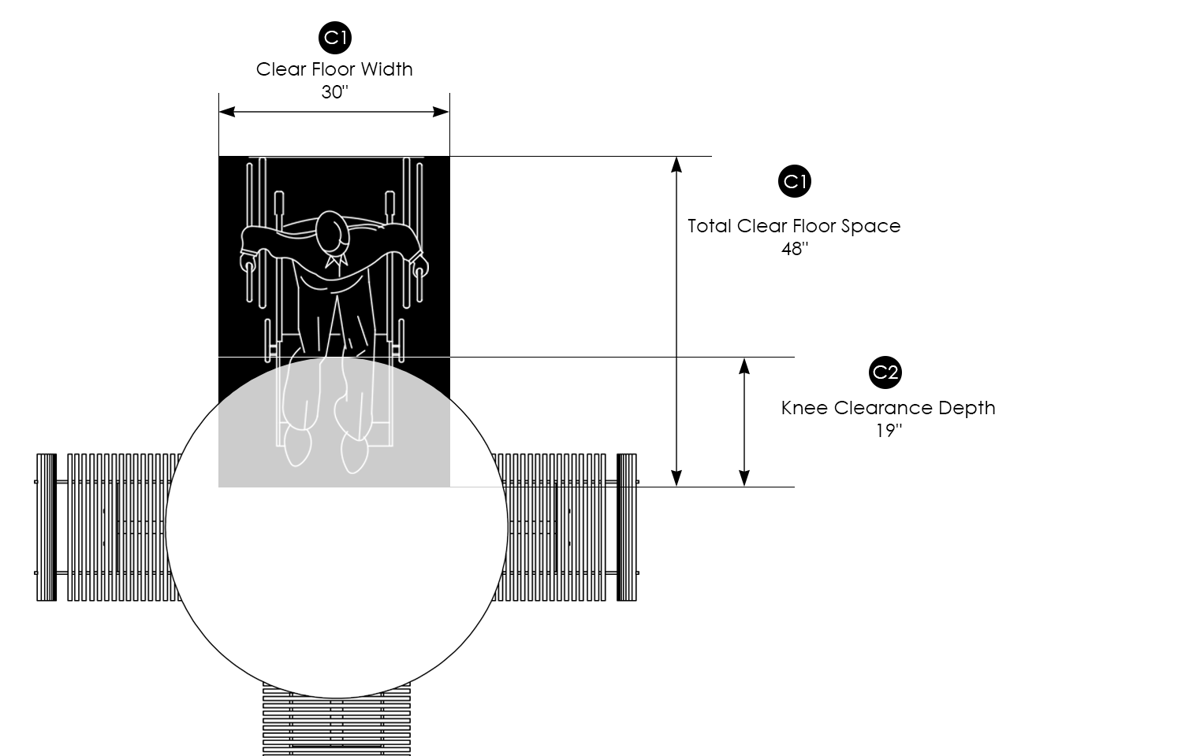
- Width and Depth: The knee clearance area must be at least 30 inches wide and 48 inches deep. These dimensions provide ample space for maneuverability, allowing users to position themselves easily and access the fixtures without obstruction.
- Clearance from Obstructions: It’s crucial to avoid placing any plumbing, electrical wiring, or structural supports within the designated knee clearance space. Thoughtful planning ensures that these elements do not interfere with accessibility.
- Sink Considerations: For accessible sinks, a knee clearance depth of at least 17 inches is recommended. This depth is necessary for users to comfortably approach and use the sink for various tasks.
Best Practices for Implementing Knee Clearance
To successfully integrate ADA knee clearance into design and construction, consider the following best practices:
- Collaborate with Accessibility Experts: Engage architects or design professionals with expertise in accessibility to ensure compliance with ADA standards and optimal usability in your designs.
- Conduct Regular Assessments: Perform routine evaluations of existing facilities to identify areas lacking adequate knee clearance. Proactive adjustments can significantly enhance overall accessibility.
- Train Staff on Accessibility Features: Educate staff about the importance of knee clearance and how to assist individuals with disabilities effectively. Well-informed staff can improve the experience for all users.
- Incorporate Adaptive Design Solutions: Whenever possible, implement adjustable features in workstations and sinks. This flexibility can accommodate a wider range of users, enhancing the overall functionality of the space.
Conclusion
Understanding and implementing ADA knee clearance requirements is essential for creating accessible environments that cater to individuals of all abilities. By adhering to these guidelines, designers and builders can enhance usability and promote independence for users with disabilities. Prioritizing knee clearance is not only about compliance with legal standards but also reflects a commitment to inclusivity and respect for all individuals. By fostering accessible and user-friendly environments, we contribute to a more equitable society where everyone can engage fully in everyday activities.
